
This article was published on Arbona Health Hub Volume 1 Issue 2 (ISSN: 3065-5544).
People of all ages, from children to adults, have engaged in video games in one way or another. The wide range of genres offers something for every preference, from classic board games to immersive battlefield simulations. Video games have become a regular part of daily life for nearly all children and adolescents, with 97% in the United States playing for at least an hour each day (Granic et al., 2014). During the COVID-19 lockdown, children spent approximately 12 hours per week playing videos games (Donati et al, 2021).
The high prevalence of video games usage is alarming and raises concerns about the potential health effects it may impose. Particularly concerning is the development of addiction and its potential effects on the musculoskeletal system. Addiction to social networks and online games has a prevalence of 32.8% among university students and may increase the risk of neck disorders (Heidarimoghadam et al., 2020). A study done among 665 university students reported that social network and online game addiction can increase the risk of wrist pain (Babamiri et al., 2018). Both findings highlight the importance of understanding how video game sessions can impact an individual’s health. Video games that involve constant wrist pressure and repetitive movements can cause entrapment neuropathies, such as Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
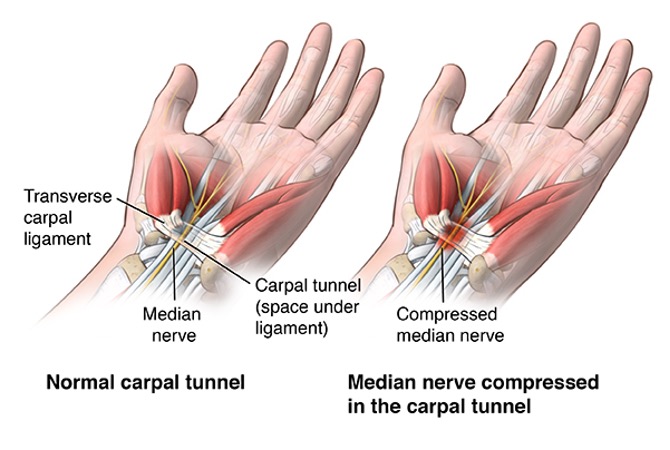
The carpal tunnel refers to a canal between the transverse carpal ligament and the carpal bones of the wrist (Figure 1). Lesions or hypertrophy in this area can compromise the median nerve found within the canal causing pain, paresthesia, hypoesthesia, and anesthesia. The pathophysiology is not fully understood, but it is believed that the increase in interstitial pressure causes ischemia and demyelination of the median nerve (Osiak et al, 2022). Recognizing the significant strain placed on the wrist during video game play, I set out to explore the current understanding of the relationship between video game usage and the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Findings
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be elicited by constant pressure and repetitive movement, often associated with electronic device usage. University students who used electronic devices for more than 5 hours per day exhibited notably higher positive results in Phalen’s and Durkan’s tests, a larger median nerve cross-sectional area, and reported increased wrist pain (Woo, White & Lai, 2017). Phalen’s and Durkan’s tests are used to evaluate median nerve compression and aid in the diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. A larger median nerve cross-sectional area may suggest nerve compression and inflammation, both being a plausible cause of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome development.
Electronic sports, commonly known as esports, athletes are the most susceptible to the consequences of video games usage. As their job involves playing video games, they devote more time to gaming than the average person. In a study consisting of 95 esports athletes and a control group of 103, those who had been esports athletes for longer periods experienced a higher score in the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire Symptom Severity Scale (BCTQ-SSS) (Basuodan et al., 2023). A higher BCTQ-SSS score suggests that players with more prolonged gaming involvement experienced more symptoms related to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, such as pain and numbness. In addition, there was a positive correlation between functional severity symptoms and hours of play. The authors also concluded that the method of play influenced the BCTQ score. Especially, the use of armrest and controllers resulted in a lower BCTQ score compared to PC gamers with keyboard/mouse.
Kendal et al. (2022) found that as game addiction score increased, esports players experienced a higher risk of musculoskeletal system discomfort and mental toughness decreased. Due to the high prevalence of Carpal Tunnel Symptoms in video game players, it is important to address which treatment options are available. Osiak et al. (2022) recommends non-surgical methods in cases of mild symptoms, however, surgical treatment is indicated in moderate to severe cases after confirmation of axonal injury. Self-myofascial stretching of the carpal ligament showed improvements in numbness, tingling, pinch strength, and symptom severity in participants diagnosed with median mononeuropathy across the wrist (Shem, Wong & Dirlikov,2020). This approach would be more accessible for gamers since it can be done without a therapist. Implementing rehabilitation practices can be essential to prevent and reduce the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome.
Conclusion
The constant pressure and repetitive movements of the wrist seen while playing video games can result in the development of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome has a positive correlation with hours spent playing video games. Mild symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome can be treated with stretching of the carpal tunnel, however, moderate to severe symptoms may require surgery. There is a need for more longitudinal studies as the prevalence of video games keeps rising. For future research, it will be crucial to explore how a video game’s genre influences the likelihood of developing Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, particularly among PC gamers, as those using a keyboard and mouse have been found to be the most prone to this condition.
References
- Granic, I., Lobel, A., & Engels, R. C. (2014). The benefits of playing video games. The American psychologist, 69(1), 66–78. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0034857)
- Donati MA, Guido CA, De Meo G, Spalice A, Sanson F, Beccari C, Primi C. Gaming among Children and Adolescents during the COVID-19 Lockdown: The Role of Parents in Time Spent on Video Games and Gaming Disorder Symptoms. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2021; 18(12):6642. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18126642
- Heidarimoghadam, R., Mortezapour, A., Ghasemi, F., Ghaffari, M. E., Babamiri, M., Razie, M., & Bandehelahi, K. (2020). Musculoskeletal Consequences in Cyber-Addicted Students – Is It Really A Matter of Health? A ROC Curve Analysis for Prioritizing Risk Factors. J Res Health Sci, 20(2), e00475–e00475. doi:10.34172/jrhs.2020.10
- Babamiri, M., Haidari Moghaddam, R., Ghasemi, F., Ghaffari, M., Razee, M., Bandeh Ellahi, K., & Mortezapour, A. (2018). Addiction to Social Networks and Online Games: A Wrists’ Pain Survey in Students. Journal of Ergonomics, 6(3). doi:10.30699/jergon.6.3.4
- Osiak, K., Elnazir, P., Walocha, J. A., & Pasternak, A. (2022). Carpal tunnel syndrome: state-of-the-art review. Folia morphologica, 81(4), 851–862. https://doi.org/10.5603/FM.a2021.0121
- Woo, E. H. C., White, P., & Lai, C. W. K. (2017). Effects of electronic device overuse by university students in relation to clinical status and anatomical variations of the median nerve and transverse carpal ligament. Muscle & nerve, 56(5), 873–880. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25697
- Basuodan, R. M., Aljebreen, A. W., Sobih, H. A., Majrashi, K. A., Almutairi, N. H., Alhaqbani, S. S., Alanazy, M. H. (2023). The impact of electronic gaming on upper-limb neuropathies among esports athletes. Med Pr Work Health Saf., 74(4), 279-287. https://doi.org/10.13075/mp.5893.01421
- Kendal, K., Ataç, A., & Köse, İ. T. (2022). Effects of game addiction on musculoskeletal system discomfort and mental toughness in e-sport players. Addicta: The Turkish Journal on Addictions, 9(2), 212-217.
- Shem, K., Wong, J., & Dirlikov, B. (2020). Effective self-stretching of carpal ligament for the treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome: A double-blinded randomized controlled study. Journal of hand therapy : official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 33(3), 272–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2019.12.002
Figure 1 Normal carpal tunnel versus Carpal tunnel Syndrome. Retrieved from https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/carpal-tunnel-syndrome

