Nowadays, we can observe an exponential growth in many neurodegenerative diseases. Previously, I had mentioned Multiple Sclerosis, and if you haven’t read the article yet, I highly recommend it. Another condition undergoing notable exponential growth is Alzheimer’s Disease. One argument posits that, thanks to resources and technological advancements, we can now diagnose diseases that have always been present in our generations. While undoubtedly contributing to the rising statistics, it’s undeniable that changes in our daily activities and our diet also contribute to various health conditions. It is said that Alzheimer’s is a growing epidemic, currently estimated to affect at least 55 million people worldwide. Without breakthroughs, projections suggest that this number could exceed 152 million by 2050. But, What is Alzheimer’s disease? How does it occur, and what cures are available on the market? I will be addressing these questions and more in this article. I invite you to express any doubts or concerns at the end and reach out to me for more information on neurodegenerative diseases.
Introduction:
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. A recent research study published in the 2023 Alzheimer’s Disease Facts and Figures report sheds light on the latest statistics, facts, and figures related to this debilitating condition. In this article, we will break down the study in a simplified format to help non-scientists understand the key findings and implications.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, characterized by a decline in memory, thinking, and reasoning skills. It is a complex condition that involves the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain, leading to the death of nerve cells and the breakdown of neural connections. As the disease progresses, individuals may experience difficulties with daily tasks, communication, and eventually lose the ability to care for themselves.
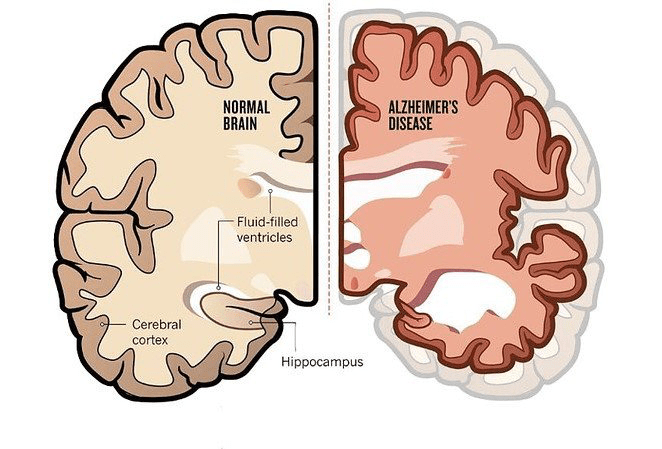
Figure 1: Visual representation illustrates the distinctive characteristics between a normal brain and a brain affected by Alzheimer’s disease. The normal brain demonstrates a balanced and well-organized structure, with clearly defined neural pathways. Conversely, the Alzheimer’s-affected brain exhibits notable structural changes, including the presence of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles, which are hallmark indicators of the disease. These aberrations contribute to the disruption of normal cognitive function and communication between brain cells, ultimately leading to the cognitive decline associated with Alzheimer’s disease. This figure serves as a visual guide to highlight the pathological distinctions between a healthy and Alzheimer’s-affected brain.
How Does Alzheimer’s Disease Occur?
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not fully understood, but researchers believe that a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors play a role in its development. The hallmark brain changes in Alzheimer’s include the formation of plaques and tangles, which disrupt communication between brain cells and contribute to cell death. Over time, these changes lead to the characteristic symptoms of the disease.
Common Symptoms to Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Memory loss: Difficulty remembering recent events, names, or faces.
- Confusion: Disorientation in familiar surroundings or with the passage of time.
- Challenges in problem-solving: Difficulty planning, organizing, or completing familiar tasks.
- Language difficulties: Struggling to find the right words, repeating phrases, or difficulties in communication.
- Poor judgment: Making questionable decisions or exhibiting lapses in judgment.
- Changes in mood and behavior: Mood swings, irritability, or withdrawal from social activities.
- Misplacing items: Putting objects in unusual places and struggling to retrace steps.
- Decreased initiative: Reduced motivation or interest in initiating activities.
- Changes in personality: Shifts in personality traits or behaviors that seem out of character.
- Difficulty in spatial awareness: Problems with judging distances or navigating familiar spaces.
Contributing Factors to Alzheimer’s Disease:
- Age: Advanced age is the greatest risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease, with the majority of cases occurring in individuals over 65.
- Genetics: Family history of Alzheimer’s and certain genetic mutations can increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, and other unhealthy habits can contribute to cognitive decline and increase the risk of Alzheimer’s.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and obesity have been linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer’s disease.
Are There Cures for Alzheimer’s Disease?
Currently, there is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease. However, ongoing research efforts are focused on developing treatments that can slow the progression of the disease, improve symptoms, and enhance quality of life for individuals affected by Alzheimer’s. The report highlights the importance of early detection, diagnosis, and access to specialized care to effectively manage the disease and support patients and their families.
In the upcoming article, I will dedicate a comprehensive and in depth exploration to unravel the mechanisms of drugs designed for Alzheimer’s disease, shedding light on the various pharmaceutical options available in the market. This detailed examination will be enriched by insights from Jessica Tang, a devoted researcher and medical student at University of California Davis School of Medicine, who has immersed herself in Alzheimer’s research since her undergraduate years. The piece will offer valuable perspectives on ongoing developments from key players in the field, including Biogen (BIIB), Eisai (ESAIY), Eli Lilly (LLY), and other prominent pharmaceutical companies, providing readers with a holistic understanding of the current landscape of Alzheimer’s medications.
As part of this landscape, following the discontinuation of its Alzheimer’s drug Aduhelm, Biogen has declared its decision to halt the commercialization of the medication. The pharmaceutical giant is strategically reallocating resources to prioritize its alternative Alzheimer’s medication, Leqembi, and actively pursuing the development of additional treatments, as outlined in a statement released on Wednesday.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, Alzheimer’s disease is a complex and challenging condition that requires a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis, treatment, and care. By raising awareness, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, and supporting research initiatives, we can work towards a future where effective treatments and ultimately a cure for Alzheimer’s disease are within reach.
By breaking down the latest research study on Alzheimer’s disease, we hope to empower individuals to better understand this condition and advocate for improved support and resources for those affected by Alzheimer’s. Stay informed, stay proactive, and together, we can make a difference in the fight against Alzheimer’s disease.
Take-Home Message:
Understanding Alzheimer’s disease is crucial for early detection and effective management. By recognizing the contributing factors, promoting a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed about the latest research developments, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. While there is currently no cure, ongoing research offers hope for future treatments that can slow the progression of the disease and improve quality of life for patients. By working together to raise awareness, support research initiatives, and provide compassionate care for those affected by Alzheimer’s, we can make a positive impact in the fight against this devastating condition. Remember, knowledge is power, and by staying informed and engaged, we can make a difference in the lives of those living with Alzheimer’s disease.
References
2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. (2023). Alzheimer’s & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, 19(4), 1598–1695. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.13016
Photo by Anna Shvets on Pexels.com


[…] Cancel Asencio provides the latest research on Alzheimer’s disease (p. […]
LikeLike